SIP Trunking – External Service Guide
Contents
Document Version 2.3
Release Date 10/02/2025
| The information contained in this document provides guidance on Colt’s SIP Trunking service and is provided for information only. It does not form part of any contract with Colt. No part of this document may be reproduced or adapted in any form, including photocopying or storing it by electronic means, except as is necessary for the purpose of the recipient’s dealings with Colt, without the written permission of Colt. Any copies made of any part of this document shall include the notice: © 2025 Colt Technology Services. The Colt name and logos are trademarks. All rights reserved. |
| No information contained in this document shall be disclosed to any third party without the written permission of Colt. |
1. Document Information
1.1 Version History
| Version | Issue Date | Reason for Change |
| 1.1 | 01.03.2016 | comments |
| 1.2 | 20.03.2017 | Updated with new product names and update appendix B |
| 1.3 | 07.10.2019 | Update Calling Line Identifier Restriction (CLIR) |
| 1.4 | 09.01.2020 | Add call termination China 9.0 and update 6.0 |
| 1.5 – 1.7 | 21.07.2020 | Add additional US states |
| 1.8 | 10.12.2020 | Add South Korea |
| 1.9 | 10.06.2021 | Update Appendix B: Country Specific Regulatory Requirements and add Hungary |
| 2.0 | 26/10/2021 | Update 6.0 |
| 2.1 | 11/10/2023 | Update 6.0 |
| 2.2 | 09/02/2023 | Update 6.0 |
| 2.3 | 10/02/2025 | Add 5.6.4 , Add 5.8.6.3 and update 9.2 |
2. Overview
COLT SIP Trunking service provides PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network ) Connectivity to customers who own or operate a IP Private Branch Exchange (IP PBX) within their organizations and want to take advantage of consolidating their data and telephony services into a single or diverse connection to the PSTN in a secure and resilient manner.
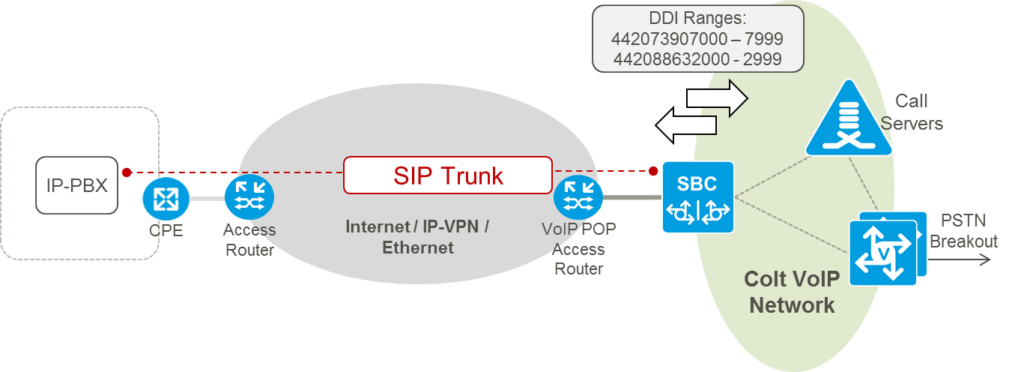
Figure 1. SIP Trunking Overview
COLT SIP Trunking has been highly regarded by both industry analysts and customers alike for the products flexibility, extensive feature set including security using SRTP and TLS, disaster recovery, performance reporting, and extensive Codec’s supported. With QoS in Colt’s network enabled as standard, customers can reliably benefit from a powerful SIP Trunking solution available from Colt with a quality customer experience and service wrap.
The Colt SIP Trunking is a product within the Voice services portfolio. Colt deliver a high quality communications service in order for businesses to maximize their efficiency and productivity, whilst minimizing their costs. SIP Trunking is a service that underpins the Colt Voice portfolio of infrastructure and managed applications including:
• Inbound & Outbound telephony services across 29 countries
• Intelligent Network-based services for advanced inbound call handling and virtual contact centre solutions
• A complete suite of hosted communication and collaboration applications
As a result, customers experience a consistent service across all their European offices reducing operational management challenges and risk. In addition, Colt offers flexible commercial models, giving customers the greater cost flexibility they are often seeking.
3. Why choose Colt?
High performance: All calls are routed over Colt’s wholly-owned, fully resilient 21st Century IP Multimedia Sub-system (IMS) network, provided by Sonus in both regions Europe and Asia. Because Colt’s core network has no voice compression, it delivers consistent, enterprise-grade call quality wherever customers operate.
Cost effectiveness: Colt’s transparent, competitive commercial options and tariff plans provide a cost-effective alternative or complement to traditional telephony, while simplification of a customer’s voice estate will generate indirect cost savings. By giving Customers the option of carrying aggregated voice and data traffic over a single connection, Colt can save customer’s even more money.
Enterprise class design: Feature-rich capabilities – no key ISDN feature left behind. Colt is not just a supplier of voice services – Colt can support Customers on a transformational journey towards a best-in-class Unified Communications environment that will support a customer’s wider business ambitions.
Superior quality: Colt’s resilient topology and saturation levels are maintained below 70% to ensure that customer traffic keeps flowing even at the busiest times.
A trusted partner: with target availability of up to 99.99%, Colt SIP Trunking is extremely reliable. Customers can trust that the service is there when customers need it.
Superior customer service: Colt’s pan-European SLA assures customers of a high levels of resilience and simplified multi-country services. Colt provide proactive voice and data monitoring 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to detect and alert Customers to any fault immediately and start early diagnosis.
Recognized by Analyst / Research companies: Colt score 4.5 out of 5.0 for SIP Trunking in Gartner’s 2015 Critical Capabilities report. Ovum positions Colt in the top 3 SIP Trunking providers in Europe
Proven SIP pedigree: More than 10 years of experience and more than 7bn minutes per year while deploying the service to more than 2000 customers in 23 countries.
4. Customer benefits
Operational efficiencies through voice and data convergence: Colt SIP Trunking enables organisations to converge voice and data traffic onto a single end-to-end IP network. This therefore allows customers to minimise the infrastructure required to carry voice calls. E.g. not requiring PSTN connections at each site.
Control over costs: Customer can reduce administration costs through simplified vendor management and by not having to build own expertise in each country.
There is a cost benefit of a converged architecture combining voice and data networks providing the highest levels of availability. Colt SIP Trunking allows voice traffic to be converged and delivered to the PSTN over Wide Area Network (WAN) links. This reduces the requirement for multiple dedicated ISDN access circuits from customer sites, and reduces the cost of Primary Rate Interface (PRI) and/or Basic Rate Interface (BRI) interface hardware by delivering a centralised service through SIP Trunking.
Through Colts Global network coverage, Colt can provide competitive call rates locally, nationally and to international destinations, to both fixed and mobile networks. Access is delivered across Colts multiple European PSTN switches.
Security and reliability: Colt SIP Trunking infrastructure is housed in multiple Colt network nodes, which are both physically and environmentally secure. All network components for the service are continuously monitored, and the service is backed by comprehensive Service Level Agreements (SLA). A number of options are available for providing resiliency in the WAN so customers can have utmost confidence in service availability and reliability. The service has been designed to perform at a target 99.99% availability (This is applicable to the SIP Trunking infrastructure only and does not include the network access elements).
Customer will retain traditional telephony features for business critical needs.
Integration & management: Colt SIP Trunking forms the basis for an integrated voice solution for organisations. It does not require the customer to change their IP PBX (or SBC) hardware, and thus disruption to end users across the telephony estate is kept to a minimum.
PBX inter-operability: We maintain a certification program with all leading PBX vendors. Customers can be confident that their IP-PBX will work with Colt’s SIP Trunking first time avoiding testing time and lengthy configuration costs
Global coverage: Continue their rapid growth as Colt expands its offer to more countries with a single point of contract and contact
5. Service Features
5.1. IP PBX interoperability testing and configuration
Customers will need to have a SIP enabled IP PBX or SBC or an IP Media Gateway in order to use the Colt SIP Trunking service. Time Division Multiplex (TDM) PBX equipment is not supported on Colt SIP Trunking but is available on Colt’s Voice Line (v).Whilst Colt SIP Trunking supports native SIP, in reality there are often proprietary extensions to these protocols added by different equipment vendors. For this reason, specific validation testing has been performed against different major software & hardware versions.
An extensive range of customer IP PBX and SBC models have been tested and validated for interoperability, and configuration guides per IP PBX vendor have been created.
General interoperability testing has been performed against IP PBX versions based on the services described in this document. This does not guarantee all features and functions can interoperate but does mean that there is a specific configuration which will provide telephony service. There are a number of IP PBX configuration guides which are available to customers to provide guidance and information on the configuration of a particular IP PBX to work with the SIP Trunking service.
Details of which IP PBXs which have been compatibility tested can be provided by a Colt sales representative.
Where PBX’s and software versions are not covered by Colt’s compatibility testing, customers can optionally make use of the Colt Engineering support service where Dedicated Engineers can support customers in getting their IP PBX connected to the SIP Trunking service. This support is targeted at any IP PBX which is not yet certified by Colt, such as: small niche IP PBX types and IP PBX vendors developing new software versions in very short intervals.
The engineer will support the customer for a given time in getting the IP PBX up and running, performing test calls, performing trouble-shooting if needed, amending configuration changes on the SIP trunk if needed or providing traces which may help Colt, the customer or the IP PBX vendor to fix issues. Colt will continue the on-going certification process of major IP PBX vendors but will enable customers with non-certified IP PBX being connected with the dedicated support of Colt Engineers as a chargeable service.
5.2. Interface Specification
5.2.1. Signalling Specification
The call control and signalling protocol of the SIP Trunking service conforms to IETF RFC 3261 and related standards for the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
5.2.2. Media Bearer Specification
The media stream conforms to RFC 1889 Real Time Protocol for the transport of voice and in-band bearer path data.
5.3. Trunk Configuration
SIP trunks are typically configured as a direct logical connection between the Colt SIP Trunking platform and the customers IP PBX (or SBC). The service does not provide a registration capability (with respective challenge authentication), but trunks are established using IP addresses to exchange SIP Signalling messages between the customers IP PBX (or SBC) and the Colt Session Border Controller (SBC).
5.3.1. Trunk & Trunk group definition
For the purposes of definition atrunk is defined as a logical entity used for VoIP signalling and media control, defined between a unique pair of IP addresses on the Colt Session Border Controller (SBC) and the Customers IP-PBX (or SBC) Equipment.
A trunk group is a logical entity that defines the grouping between one or more trunks, belonging to the same customer, that share the same DDI telephone number ranges and other parameters such as call admission control, and other features described in this document.
5.3.2. Multi-Country deployments
For customers who are located in multiple countries, in order to support national dialling formats, network tones, numbering and number portability, and emergency services access, individual trunks (or trunk groups) per country must be created.
5.4. Connectivity and determining bandwidth requirements
5.4.1. WAN Access options
A suitable WAN or Internet Access service is required in order to connect to Colt SIP Trunking – the following access types are available:
- Dedicated connection – provided by Colt solely for the transport of VoIP signalling and traffic, based on MPLS IP VPN – Access via a Colt IP Virtual Private Network
- Colt IP VPN via NNI
- Colt IP Access
- 3rd Party Public Internet
Customers are responsible for the specification, provisioning and maintenance of their own Local Area Network (LAN) infrastructure. This infrastructure must be of a suitable standard to prioritise voice traffic and ensure QoS as well as passing SIP signalling and RTP for establishing voice calls.
The link between the customer’s premises and Colt needs to be dimensioned and configured correctly in order to maintain a good quality of service. Please see section 3.4.2 with respect to guidance on how much bandwidth is required per concurrent call. The maximum required number of simultaneous calls during the busiest time of the day (the “busy hour”) between customer sites and the PSTN will determine the bandwidth required. Colt can help customers with this design.
5.4.1.1. Dedicated Access
If customers do not have an existing Colt data access service in place or require a dedicated connection for voice only services, then connectivity can be provided as part of the SIP Trunking service. This connection can be with a dedicated MPLS based Layer 3 connection capable of carrying only VoIP traffic for high bandwidth high call volume requirements (up to 10Gbps). All the connection bandwidth (less 10% for signalling and management) may be used to carry Colt SIP Trunking traffic. The following delivery options are available:
- Colt ‘Fibre to the Premise’ connection (referred to as On-net)
- 3rd Party leased line access (referred to as an OLO tail)
- Colt DSL (where available Colt deliver over an Unbundled Local Loop)
- 3rd party DSL (Wholesale DSL) – where Colt uses DSL access from a wholesale provider for nationwide coverage. Typically only uncontended options (often labelled as 1:1 contention ratio) are used to ensure performance quality of the service.
5.4.1.2. Colt IP VPN
This is Colt’s private IP network, delivered over an MPLS network and called Colt IP VPN Corporate Plus. All bandwidth options of 1Mbps and above are available. On DSL based access customers should only use uncontended options (often labelled as 1:1 contention ratio) to ensure performance quality of the service.
Voice and Data services can be converged together over Colt IP VPN. If customers are planning on converging voice and data on the VPN, a maximum of 50% of the total bandwidth can be allocated to voice due to limitations in IP VPN priority queuing. This limit is based on all VoIP traffic routed through the highest priority low latency class of service.
5.4.1.3. Colt IP VPN via NNI
The IP VPN for SIP Trunking can also be routed through an existing MPLS NNI (Network-Network-Interconnect). This allows Colt to provide service via other Carriers direct to customers who have an existing IP VPN service. Using this NNI, Colt only needs to create logical trunks through this connection. The NNI bandwidth options are 100 Mbit or 1Gbit. It is necessary to contact a Colt Account manager to confirm that a NNI is in place with a current network provider.
5.4.1.4. Colt SD-WAN
Colt SDWAN is an overlay VPN solution. SDWAN CPEs deployed on customer sites establish an encrypted overlay VPN or Internet and/or MPLS connections. Customers can configure traffic policies to control which path traffic is routed over based on real-time SLA monitoring between sites. SDWAN gateways ensure sites on different transport networks can reach each other and provide the ability to breakout from the SDWAN overlay onto a traditional MPLS-based IP-VPN service
VoIP over SDWAN can be offered using existing capabilities.
5.4.1.5. Colt IP Access
Colt IP Access (Colt’s internet access product) provides a direct connection to Colt’s, uncontended, IP backbone where it is unlikely performance will be compromised by delay or packet loss. Bandwidth options of 2Mbps and above are recommended for Internet access based connections to maximise the probability of acceptable quality. For optimal performance on DSL based access technologies customers should only use uncontended symmetric options (often labelled as 1:1 contention ratio) to ensure performance is optimised. Additionally Colt recommend that priority queuing is configured within the customers network.
5.4.1.6. 3rd Party Public internet
Colt SIP Trunking is available over 3rd Party public IP networks which do not restrict any of the port or application types used for VoIP. In general using public internet based access should be approached with caution as Quality of Service is not available which may lead to degraded VoIP quality. Due to the unpredictable performance of public IP networks (which do not have Quality of Service) no service level guarantees can be provided for SIP Trunking performance and speech quality. Service over the Internet is provided on a ‘best effort’ basis. Due to the nature of the Internet there is no Quality of Service, which means there may be performance impairment between the 3rd party ISP and Colt’s SIP Trunking platform.
So, operating SIP Trunking traffic only on the access does not guarantee quality and cannot be supported by an SLA.
For Non-Colt (public) internet access then the following guidelines are recommended:
1. The Internet connection must only be used for SIP Trunking traffic, no Internet traffic may be sent. This is to minimise the impact of contention between voice and data on the access link.
2. If voice is critical to a customer’s business operation, then Colt recommends using an access method with Quality of Service and un-contended bandwidth such as Colt IP Access.
5.4.2. Bandwidth Requirements
It is very important to ensure that the bandwidth allocated between the customers IP Telephony end-points and the Colt SIP Trunking platform is sufficient for the peak number of calls required. If this is not carefully dimensioned then voice quality will degrade. Typically the access connection to a site is the limitation of bandwidth. The following table can be used as an approximation to the amount of bandwidth used per call. (Note: variations due to access type and use of encryption may make figures vary):
| Codec | Bit rate Payload (kbps) | Sampling Rate (ms) | Bandwidth per Call at Layer 2 (kbps) |
| G.711 | 64 | 20 | 95.2 |
| G.729 | 8 | 20 | 39.2 |
| G.729a | 8 | 20 | 39.2 |
| G.726 | 32 | 20 | 63.2 |
| iLBC | 15.2 | 20 | 46.4 |
| G.722 | 32 | 20 | 63.2 |
| T.38 | 20-100 | n/a | 20-100 |
Note: T.38 is the standard for the conveyance of Fax over IP. Please see section 3.6.5 for further information.
The following formula provides the peak number of calls that can be carried for a given access bandwidth (10% of bandwidth must be reserved for signalling and management):
Peak Number of Calls = [ Available access bandwidth] / [bandwidth per call x 1.1]
5.5. IP Design
5.5.1. Colt Dedicated, Colt IP VPN, Colt IP VPN via NNI, (Private IP Addressing)
All addressing must be provided by the customer from within their own private address space. Therefore customers should provide Colt with /27 private IP ranges for each Colt VoIP Point of Presence (V-POP) where the customers SIP Trunk shall be connected to. This subnet is configured on the Colt V-POP , and is used to allocate signalling and media IP addresses on the Colt V-POP, so that they are reachable from the customers network.
5.5.2. Colt IP VPN supported Routing Protocols
For IP VPN, Static Routing, Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2), and Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 (BGPv4) are supported.
5.5.3. Colt Dedicated, Colt IP VPN, via NNI,IP access design guidance.
Customers should note that a maximum of 26 trunks per /27 IP address range are possible. Where customers require more than 26 trunks and/or operate one or more IP PBX’s then the following configurations are possible
5.5.3.1. Multiple Trunks on same POP – Individual PBX IP address per Trunk
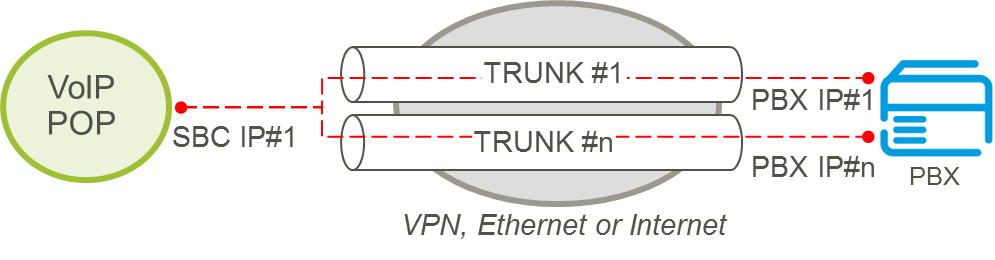
An individual IP PBX IP address is configured per trunk and the same V-POP IP address is used by all trunks. This is the default configuration for customers with multiple trunks on same V-POP.
5.5.3.2. Multiple Trunks on same POP – Single IP PBX IP Address
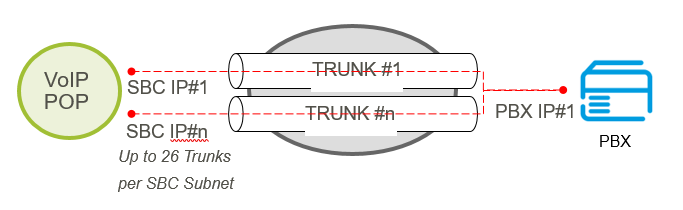
An individual SBC IP address is configured per trunk and the same IP PBX IP address is used by all trunks. This option is only supported for customers with a VPN connection.
5.5.3.3. Trunks on different POPs – Single PBX IP Address
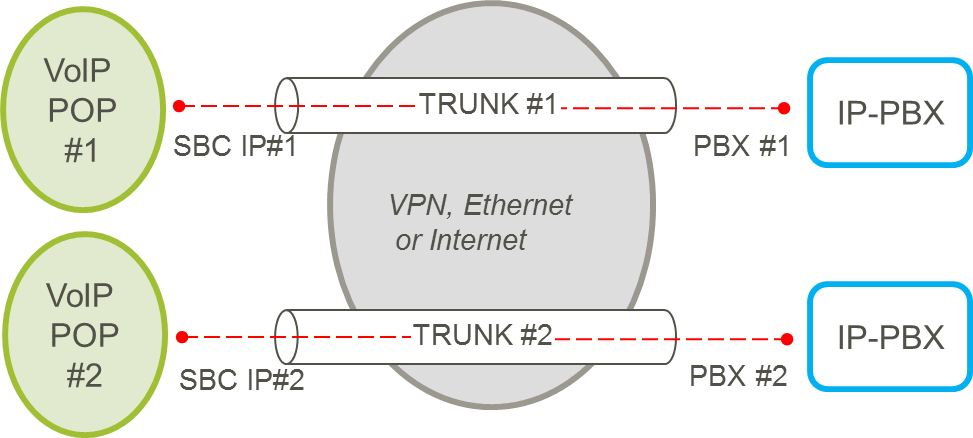
An individual SBC IP address is configured per POP and the same PBX IP address can be used by all trunks. For additional trunks, the same rules as the single POP scenarios apply.
5.5.4. Reserved IP Addresses for Colt Dedicated
In order for Colt to manage the service as well as provide WAN connectivity across the network, Colt shall use the 10.82.0.0/22 address space for management. It is not possible for customers to use any of these addresses on their own networks, therefore Colt shall require Customers to change their network addressing configuration if this range is currently in use.
5.5.5. Access over Public IP
5.5.5.1. Overview
The Colt SIP Trunking platform has public IP addresses for connection over the Internet. If Customer endpoints and the IP PBX have public addresses then they will be able to communicate directly with the platform. However, it is more normal to have the IP PBX and endpoints within a privately addressed network, which is connected to the Internet via dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT) or Port Address Translation (PAT). In such cases these require a specific configuration to ensure that the Colt SIP Trunking platform can communicate with the IP PBX behind the NAT device.
5.5.5.2. Additional Trunk Requirements
Where a customer requires multiple trunks to be delivered across the internet, customers must therefore allocate additional public IP addresses per trunk required, or by using multiple NAT instances as the diagram shows below:
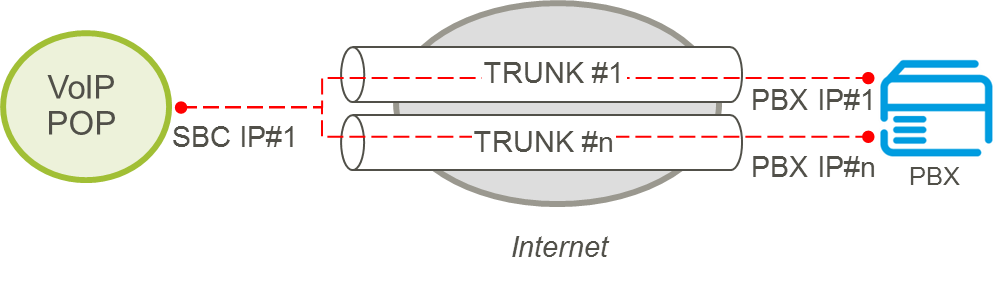
5.5.5.3. NAT on CPE router:
The role of the CPE Router is to connect the Customers Local Area Network to the Internet, and provides a logical demarcation point. Internet access terminated on a router which has ‘N:1 NAT’, also called PAT (or overload NAT), is usually configured to provide connectivity for internal devices to the public Internet via a shared public IP address. This NAT method implies that initial request is made from the internal side to the internet (e.g. a PC connects to a web-server). For a SIP Trunking to IP PBX call, it is necessary to configure a static NAT entry on the CPE router which points to the IP PBX. Customers should either request this from their service provider if the CPE performing the NAT is managed, or implement a configuration on their own router performing the NAT. The CPE router is configured to forward traffic received on a given port on the public WAN interface to the IP Address of the IPPBX on the internal side. For a SIP trunk this means that ideally the UDP port 5060 (the standard SIP port) should be used on the WAN side to identify packets which must be translated to the IP address of IP PBX. (Other ports could be used as well but since Colt need to know the port number for SIP Trunking platform configuration it must be provided on the order form (in addition to the IP PBX address).
Example:
[Colt] -> [CPE Public Address] -> [IP-PBX Private Address]
80.80.80.1:5060 -> 10.10.10.10:5060
Also if a NAT on a CPE cannot port forward based on UDP port 5060 then a different port number can be used, for example, using port 6000 on the WAN side would give the following mapping:
[Colt] -> [CPE Public Address] -> [IP-PBX Private Address]
80.80.80.1:6000 -> 10.10.10.10:5060
(port 6000 on CPE forwarded to SIP port 5060 on IPPBX)
The NAT function on the CPE must not be ‘SIP aware’, it must not change any SIP signalling data.
NOTE: Where an alternative port number is used, this must be specified at point of order by the customer.
5.5.6. Quality of Service
It is important to ensure voice quality that overall IP quality of service parameters are not exceeded between End-points to SIP Trunking Platform. The following table forms a guide to follow:
| Parameter | Maximum value |
| Latency (Round trip) | 150ms |
| Jitter | 20ms |
| Packet loss | 1 in 10E3 (or better) |
The Colt network will not add more than the following to the overall end to end performance budget for IP VPN access (these figures do not apply to DSL based access):
| Parameter | Value |
| Latency (Round trip) | 30ms |
| Jitter | 10ms |
| Packet loss | 1 in 10E6 |
This is for trunks terminating in Europe delivered over Colt data network.
5.5.7. IP Version 6
The SIP Trunking service can support IP Version 6. This is ordered using the standard Colt order form process, but specifying specifically that IP Version 6 is required.
5.6. Signalling and Media capabilities
5.6.1. Voice Coding
Customers should choose the CODEC which is used between the IP PBX and the Colt SIP Trunking service (the choice of CODEC determines the extent to which speech is compressed within a VoIP network). The CODEC recommended by Colt for use with SIP Trunking is G.711a with 20 millisecond sampling rate.
Supported Codecs are:
| Codec | Recommended sampling period | Remarks |
| G.711Alaw | 20ms | Uncompressed Codec with very good call quality |
| G.711µlaw | 20ms | Uncompressed Codec with very good call quality |
| G.729 | 20ms | Highly compressed Codec with good call quality |
| G.729a | 20ms | Highly compressed Codec with good call quality |
| G.726 | 20ms | Compressed Codec with good call quality |
| iLBC | 20ms | Highly compressed codec with good call quality |
| G.722 | 20ms | HD wideband codec transmitting 7khz audio |
5.6.2. Transcoding
It is possible to use any of the above Codec’s shown in 3.6.1, but to avoid transcoding for IP-IP calls, customers are recommended to support G711Alaw 20ms codecas a fall-back. If customers cannot support the G711Alaw codec then Colt can provide a transcoding capability, however this is a chargeable feature, and is calculated based on the maximum number of concurrent calls configured on a trunk.
5.6.3. Call Admission Control
Colt places limits on the number of simultaneous media streams (calls) across a trunk. Call admission Control (CAC) is implemented in order to manage the bandwidth more efficiently and to reduce the overloading of connectivity. Customers therefore must specify a value for the maximum number of simultaneous calls.
This capability does not replace the implementation of CAC on the customers IP PBX, which Colt recommends is also used. Colt’s CAC capability feature is based on a specific trunk at trunk level only, and not at an individual access connection (as an entity) – therefore where there are 1 or more trunks on an access connection this must be taken into account.
Customers may also specify the split of incoming / outgoing calls on a given trunk.
1. Call Admission Control Options
Call Admission Control (CAC) is applied to a trunk and defines the maximum number of concurrent calls that can be supported. The following options are available:
Bi-Directional CAC: Defined as the maximum number of concurrent calls on the trunk irrespective of the call direction.
Directional CAC: This allows the maximum number of inbound calls, and the maximum number of outbound calls to be applied, with an overall call limit to be separately defined on the trunk.
NOTE: The default Trunk Call Admission Control maximum limit is 300 concurrent calls in either direction. Where customers require more than 300 concurrent calls a capacity planning check is required to ensure that capacity is available, and add capacity if required.
5.6.4. concurrent Call Pool (CCP)
Apart from call admission control, this feature will allowed to configure combined CAC limit among the two or more Trunks configured in the same SBC. Share pool CAC limit and individual CAC limit together will decides number of call allowed through the trunk. E.g Shared pool limit is assigned as 15, between two trunks and individual call limit is 10, then concurrent calls between two trunk will not exceed 15 and for single trunk there will not be more than 10 calls are permitted.
5.5.5. Encryption
SIP Trunking provides both SIP signalling and audio encryption. Encrypting the signalling through SIP TLS (Transport Layer Security) only can be ordered, but for complete security, customers can secure the audio stream with SRTP (Secure Real-Time Protocol) media encryption.
For TLS, Colt supports TLS Version 1.2 (or earlier) with mutual authentication using port 5061. Both Asymmetric Encryption (AES) and Triple Data Encryption (3DES) are supported.
Secure RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is an IETF cryptographic protocol used to provide secure communications over an un-trusted network. SRTP uses RFC3711(SRTP) and RFC4568(SDES). The latter is used for exchange of cryptographic keys used to establish the SRTP session. It provides confidentiality and message integrity for RTP media streams over packet call legs.
Encryption authentication is based on the exchange of certificates. The customer is responsible for obtaining the certificate to be installed on their own equipment.
Public certificates are then exchanged by Colt and the customer and used to establish a TLS session. SRTP key exchange occurs within the SIP session (using SDES) and is encrypted using the TLS session.
5.6.6. Fax
The ITU standard of T.38 for the conveyance of Fax over IP is the recommended method for use with Colt SIP Trunking. As an alternative, sending faxes in an in-band G.711Alaw call may be used, but not recommended.
NOTE: Where the usage of fax is for business critical needs, then Colt recommend that analogue exchange lines are used .
5.6.7. Modem
Modems are rarely used on IP Telephony systems and are not recommended to be used over the service. The only method is to use G.711 codec and carry modem within the voice codec (G.711Alaw modem-pass-through), however, this will only have a limited connection speed which may be unsatisfactory for the application required.
If modem transmission is a critical part of a customer’s needs then Colt recommend the use of a traditional PSTN line.
5.6.8. Video Calls
Carrying video calls currently is not supported.
5.6.9. Digital Data Transmission
Digital data transmission including 64kbps Unrestricted Data (URD) is not presently supported.
If customers require such a capability, then Colt recommends using a separate ISDN line.
5.6.10. DTMF
The following methods are supported to carry DTMF tones:
| DTMF Method | Description |
| RFC2833 | For SIP DTMF transferred as Named Telephony Events in RTP payload |
| RFC 4733 | RTP Payload for DTMF Digits, Telephony Tones, and Telephony Signals |
5.7. Supplementary Services
5.7.1. Direct Dial In (DDI)
Incoming calls to any of the allocated numbers against the PBX trunk are typically delivered for Called and Calling Party Number in E.164 with “+” prefix format. Other number formats are supported upon request.
5.7.2. Direct Dial Out (DDO)
For SIP trunks numbers must be sent ‘enbloc’.
The default format for Called Party Number and Calling Party Number is e.164 with “+” prefix. Other types of formats are supported upon request.
5.7.3. Calling Line Identifier Presentation (CLIP)
Colt SIP Trunking service screens the calling party number to ensure it conforms to the PSTN numbers allocated to the trunk or trunk group. Should the number sent not exist within the allocated number range or a number parameter is not present then Colt shall insert the main number of the allocated range (or the default number). In addition the call shall be rejected, where the customer trunk has more than one local area code allocated.
5.7.4. Calling Line Identifier Restriction (CLIR)
A calling party number may be marked as restricted to prevent presentation to destination parties. This can either be done by the following methods:
- An IP PBX sending a P-Asserted-Identity header and Privacy: ID header (as per RFC3323/RFC3325 or using the Anonymous Form header e.g. sip:[email protected] (As per RFC3323)
- An IP PBX sending (via user dialling) a country specific prefix to the called party number (where available):
| Privacy | Country |
| 141 | UK / Ireland |
| 067 | Spain |
| #31# | US, Australia, Germany, France, Denmark, Italy, Netherlands, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland |
| 3651 | France |
| *67# | Italy |
Optionally, it is also possible to set the calling party number to be always restricted.
5.7.5. Presentation Number
Colt support the population of the Generic Number (otherwise known as Presentation Number in certain protocols) based on using the calling party information supplied from the customer when this falls within agreed ranges which are allocated to the customer. Within the Colt network the Generic Number is used as the primary information to deliver the calling line identification to the called party for display purposes.
Where calls terminate off the Colt network then, where supported in the network to network signalling systems, Colt will send the Generic Number in the call setup messaging to the transit or termination network. In many cases the termination networks support the transport and mapping of Generic Number for calling line identification and display purposes. However, there are networks and service platforms (e.g. Voice Mail platforms and PBXs/handsets) which do not transport or utilise the Generic Number information and therefore it’s support and use cannot, if any calling line identification, to be used. The network number is the service provider assigned number associated to the service from which the call originates. It has to be fixed by the service provider as it has legal and commercial considerations for the telephony services (such as identification in call trace scenarios).
This feature is only available in Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland, and the UK but is subject to country specific regulatory requirements as to what the presented number can be set as. For further information please see Appendix B.
5.7.6. Calling Line Identification Presentation no Screening
Calling Line Identification Presentation no Screening allows an alternative CLI (other than the customers permitted ranges configured at the trunk group level) to be sent for display purposes. The alternate CLI should be included in the SIP From header. As this feature utilises the Generic Number capability, the same limitations, of guaranteeing its transport across networks, apply as with presentation number. This feature is only available in Austria, France, and Germany, but is subject to country specific regulatory requirements as to what number types can be presented. There are some specific use cases where this feature can and cannot be implemented, therefore Colt advises that customers contact their sales representative for further guidance. For general country information please see Appendix B.
5.7.7. Special Supplementary services
Due to dependencies on termination at the called party side, we do not support commit supporting the following supplementary services:
COLR (Connected Line Identification Restriction), COLP (Connected Line Identification Presentation), CNIP (Calling Name Presentation), UUS (SIP-I, User-to-User Signalling), MCID (Malicious Call Identification), CCBS (Completion of Calls to Busy Subscriber)
5.7.8. Emergency calls routing
As a fully compliant and regulated telecoms provider, Colt provides full emergency services access. Therefore when a call is made from an IP PBX to an emergency services access number, Colt shall route this to the appropriate emergency services operator based upon the address assigned to the calling party, and in the case of multi-country customers against the appropriate trunk.
Please note that service in Japan does not currently support emergency call handling.
5.7.9. Other Supplementary Services
In general SIP Trunking should be transparent to supplementary services implemented on the customer IP PBX.
Supplementary services requiring interaction with the network are not supported at this time. Call forward and diversion may populate the Redirection number parameter (in SIP this is called the diversion header) to show the number of the call diverting, however for this to pass network screening the full national significant number should be sent.
5.8. Resilience
5.8.1. Resiliency Order
SIP Trunking resiliency operates in the following hierarchal order
- Access resiliency
- Trunk / V-POP resiliency
- Inbound Call Re-routing and Partial number replacement
5.8.2. Access Resiliency
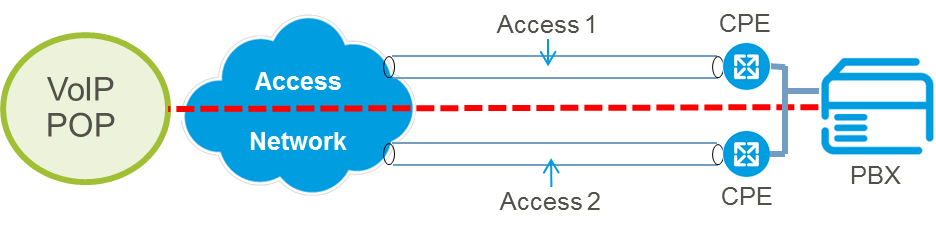
Colt’s SIP Trunking dedicated connection and Colt’s data services offer dual connection options to a site with ‘hot-standby’ configuration to provide automatic switchover in the event of loss of one connection. This maintains the service without any change of the logical signalling trunk or media addresses.
5.8.3. Trunk Resiliency
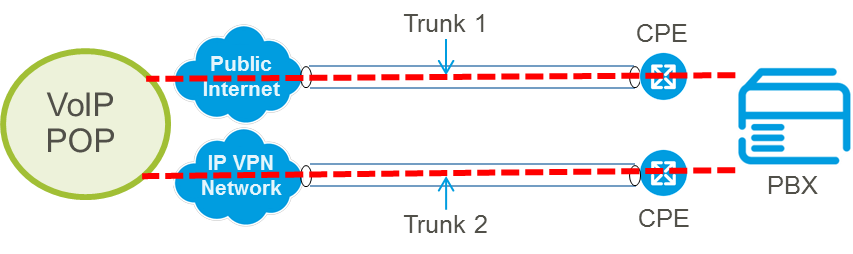
Trunk level resiliency enables customers with the ability to switch between trunks which, for example, can switch delivery across multiple access types (such as a IP VPN and internet), in order to route traffic appropriately in the event an access connection failing or to support a resilient IP PBX cluster. The diagram above shows access resiliency across an IP VPN as the primary method of access with Internet access as the secondary with resilient trunks split across them.
Trunk resiliency can be configured on a resilient or non-resilient access. The diagram below shows an example of resiliency being provided at trunk level (trunk resiliency) with a non-resilient access.
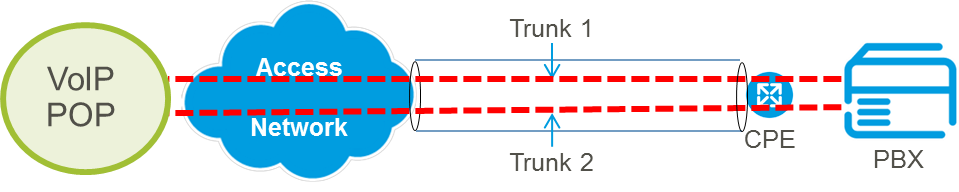
Inbound calls as standard will be delivered to the first trunk within the trunk group in a sequential pattern (please see section 3.8.5 for alternative trunk group call distribution patterns). Should an inbound call fail to be delivered to the first trunk, the first trunk shall then be taken out of service for 3 minutes (otherwise known as “black-listing”), and inbound calls shall be delivered to the second trunk. After 3 minutes, a call attempt shall be made again to the first trunk, and if successful, inbound calls will again automatically be delivered to the first trunk. If the call however is unsuccessfully delivered to the first trunk again, the first trunk shall be black-listed again, and the second trunk will be used. This process will be repeated until the first trunk is able to successfully receive inbound call attempts, and upon a successful inbound call, all inbound calls shall be delivered to the first trunk. Where customers have more than two trunks, inbound calls will be delivered to the next available trunk if the previous trunks are un-reachable they are black listed in sequential order, unless an alternative trunk group distribution pattern has been requested (please see section 3.8.5).
For outbound calls from the customers IP PBX, it is the customers’ responsibility to fail over to an alternative trunk. Customers can use SIP OPTIONS to detect the availability of trunks, which should then determine which trunk should be used.
SIP OPTIONS may be used to detect when a trunk has failed and becomes available again. In this mode of operation, the SIP Trunking platform sends SIP OPTIONS messages to the customer IP PBX. SIP OPTIONS are sent every 20 seconds, and if they are not responded to from the IP PBX, the trunk remains out of service until a 200OK is received. When a 200OK is received, the trunk is brought back into service and subsequent calls can be delivered to the trunk. This method ensures faster recovery when connectivity is restored but requires the customer IP PBX to support SIP OPTIONS.
NOTE: The use of SIP OPTIONS is not currently a standard option and Customers must speak to their Colt representative to request this method of implementation.
5.8.4. VoIP Point of Presence (V-POP) Resiliency
SIP Trunking provides an option for customers to be connected to geographically separate V-POPs (SBCs), using multiple trunks to each POP. In the event of failure of the primary V-POP, Colt enables the automatic routing of traffic via the secondary V-POP. In addition it is possible to provision multiple Trunks to either one or more V-POPs and to one or more IP PBX’s on the customer sites (or customer SBCs). By default where a customer has implemented Trunk resiliency, the second trunk shall be provisioned to an alternative V-POP to the primary trunk, and therefore an additional /27 address space is required for each V-POP for all access types except Colt IP Access and 3rd Party internet connected customers.
POP resiliency can be configured on a resilient or non-resilient access.
5.8.5. Trunk Group Call distribution Pattern
For trunk and V-POP level resiliency the following load sharing call distribution patterns are possible across trunks:
- Sequential
- Round Robin
- Proportion
A trunk group is defined as a group of individual SIP trunks.
Sequential will deliver all calls to the first trunk within a trunk group until the defined Call Admission Control value has been reached. If this trunk becomes unavailable / unreachable, then the SIP Trunking service will search for the next available trunk within the trunk group. Hunting will take place according to the order in which the trunk IP addresses are provided when the service was ordered. There is a 3 second switchover recovery time before calls are re-routed to the secondary (and subsequent) trunk. In addition with the usage of Call Admission Control (CAC), calls shall overflow to the secondary (and subsequent) trunk, where the CAC limit has been reached.
Round Robin will deliver calls evenly across all trunks in the trunk group. Inbound calls are therefore ‘load balanced’ across the trunks.
Proportional configuration allows customers to define the call distribution among the trunks within the trunk group, and this is very useful when customers have more than two trunks, for example a PBX has 3 trunks configured in resilient mode, however due to bandwidth constrains, the 1st trunk should take 60% of load, the second 30% and the 3rd only 10%.
It is therefore worth noting that Round Robin is a specific configuration of Proportional.
For outbound calls, the customer should decide how to distribute calls across the available trunks. If a trunk becomes unavailable or unreachable, then the customer is responsible for re-routing calls onto the next available trunk. Customers can use SIP OPTIONS to detect the availability of trunks, which should then determine which trunk should be used.
5.8.6. Inbound Call Rerouting & Partial Number Replacement
5.8.6.1. Inbound Call Re-routing
Colt offers a feature with SIP Trunking known as ‘Inbound Call Re-routing’. When loss of connectivity occurs and no trunks are available between the Colt SIP Trunking platform and the IP PBX, all inbound calls to the customer may be automatically redirected to a single E.164 number specified by the customer. This E.164 number must be specified in advance, via the product Order Form. It can be:
- A Colt provided E.164 number, associated to a Colt TDM circuit or Colt SIP trunking service. In the latter case, the E.164 number must be associated to a totally different Colt SIP trunking service for the feature to work
- A Non-Colt provided E.164 number (associated to a non-Colt voice service)
5.8.6.2. Partial Number Replacement
Partial number replacement allows the automatic number manipulation for inbound calls (Colt to customer) to be routed to pre-defined alternative numbers whilst preserving the extension number details. For example calls to the number range of 020 7390 1000-2000 would be re-routed automatically to 020 7450 1000-2000 in the event of loss of connectivity. This feature is activated when no configured trunks are available to route calls to the customers IP PBX. The lines associated with the alternative numbers may be any PSTN number not necessarily part of the SIP Trunking Service, nor belonging to Colt. As with inbound call re-routing, the range start and range end of the numbers being replaced must be specified in advance via the product order form.
5.8.6.3. Call Diversion features
Inbound Call Re-routing And Partial Number Replacement
Inbound call re-routing (ICR) and Partial Number Replacement (PNR) are call diversion features that allow calls to be automatically forwarded to a preselected number or number range in the event that a trunk is down due to connectivity failure.
These features are only invoked when all trunks (primary and secondary) are down due to non-reachability. The same trunk failure detection and recovery mechanisms apply.
Call Forwarding Unconditional
This feature is similar to Inbound call re-routing, when invoked calls will be diverted to a pre-selected number always, It does not wait for any response from remote end. Forwarding number is always preselected (Pre-configured) and mapped to a single or multiple DDI number(s).
Call Forwarding on Busy
This feature allows call to be diverted to a preselected number, when remote end response in busy. Forwarding number is always preselected (Pre-configured) and mapped to a single or multiple DDI number(s).
Call Forwarding on No answer
This feature allows call to be diverted to a preselected number, when remote end does not answer, till answer timer expires. Forwarding number is always preselected (Pre-configured) and mapped to a single or multiple DDI number(s).
Call Forwarding on No answer and Busy
This feature allows call to be diverted to a preselected number, when remote end does not answer, till answer timer expires or remote end response is busy. Forwarding number is always preselected (Pre-configured) and mapped to a single or multiple DDI number(s).
5.8.6.4. Feature Operation
The features described previously are automatically revoked when communication between the SIP Trunking platform and the customers IP PBX (or SBC) is restored. The operation of these features is as follows:
- An inbound call attempt to the customers IP PBX is made over the configured trunks.
- If the connection to the IP PBX has failed then either a SIP INVITE transaction timeout (2 attempts) or a TCP connection timeout occurs, and the call is then re-routed to the backup number or number range defined which is configured on the customers trunk.
- Subsequent inbound calls are re-routed to the backup number or the number range following the same timeout mechanism until connectivity is restored.
- When connectivity is restored, inbound calls automatically revert to the customer IP PBX (or SBC).
Note: When inbound call re-routing or partial number replacement is combined with trunk resiliency, the failure detection and recovery mechanism of the trunk resiliency feature takes precedence. In other words the trunk resiliency mechanism shall be used first until no trunks are available, and then at that point the above features described shall be invoked. Please refer to section 3.8.3 for further details.
5.9. Disaster Recovery
A customer’s disaster recovery planning is managed with two options – IP Address re-routing and TDM re-routing otherwise known as DDI based disaster recovery.
5.9.1. IP Based Disaster Recovery
IP based disaster recovery allows the manual diverting of a signalling trunk and media address to a different IP address. This IP address can be a 3rd party public IP address if necessary. The diagram below illustrates this:
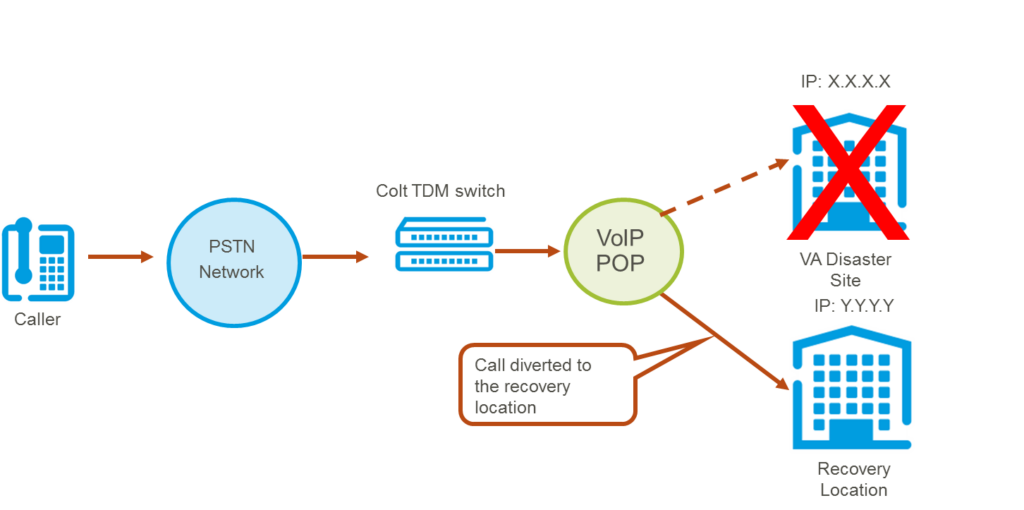
IP Based Disaster recovery is useful for customers where they require logical re-routing of a Colt SIP Trunk to another IP PBX platform in a manual condition, for the purpose of business continuity.
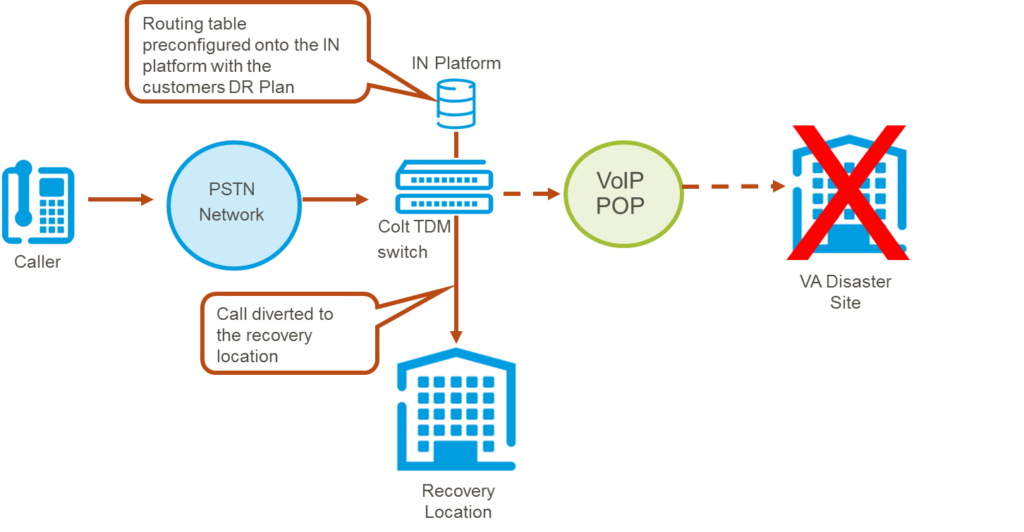
5.9.2. DDI Based Disaster Recovery
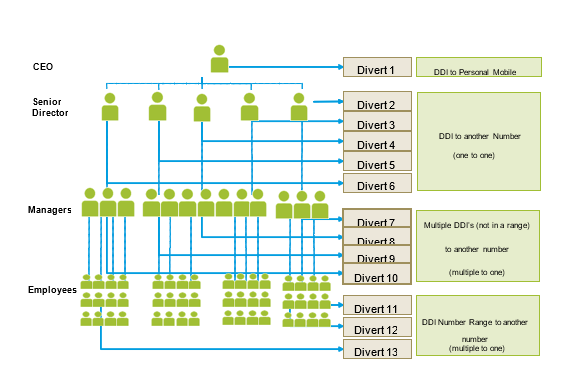
DDI based disaster recovery enables customers to divert incoming calls to pre-defined PSTN telephone numbers. A divert can be either a single number diverted to another number, or a single contiguous range of numbers diverted to another single number. For example a contiguous range such as 020 7390 1000-2000 would be diverted to 020 7450 1000. A maximum of 5 disaster recovery plans can be defined and will be activated after calling the Colt helpdesk and authorizing one of the plans. Each plan can hold up to 90 diverts, which can be a combination of a single number divert to another number, or a contiguous range of numbers diverted to another single number. The diagram below explains this capability:
The diagram below shows an example disaster recovery plan implementation:
5.9.3. Testing and ordering
Any DR option needs to be specified in the ordering process and needs to be tested to ensure the correct operation of the disaster recovery plan, before Colt can apply and comply to the disaster recovery service level agreements (DR SLA). Once a disaster occurs and the activation of the disaster recovery plan is required, the customer must call the Colt Helpdesk, authenticate themselves by providing there name, telephone number, and pre-defined password and then request activation of the relevant disaster recovery plan.
5.10. Performance Reporting
5.10.1. Overview
Performance reporting provides customers with near real-time statistics on the SIP Trunking service via an online portal accessible through the Colt Online customer portal.
The following diagram shows how performance is measured:
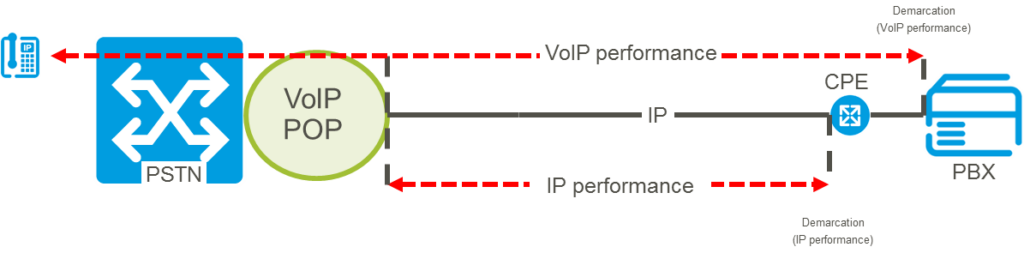
VoIP Statistics are available across all access types. IP Statistics are only available on a dedicated MPLS based Layer 3 access connection, or for Colt IP VPN connections via the service performance portal from the Colt CPE.
For SIP Trunking service provided via a dedicated IP VPN connection, the online portal shows IP level statistics and Voice statistics described as in the following sections.
5.10.2. IP Statistics
The following network performance statistics are available to allow customers to see the performance of their IP connectivity to the SIP Trunking service with appropriate measures:
- Jitter – measured in milliseconds (ms)
- Round Trip Delay – measured in milliseconds (ms)
- Reachability – measured in percentage terms (%)
- Packet Loss – measured in percentage terms (%)
- MOS – Mean Opinion Score, calculated based upon the latency, packet loss, and jitter.
Customers can find further information on the IP statistics available from the Colt IP VPN Performance reporting user guides which is available from their Colt account manager.
5.10.3. VoIP/Voice Statistics
Customers can measure the inbound and outbound voice performance of their SIP trunks using the following statistical measures:
- Answer seizure ratio – measured in percentage terms (%)
- Network efficiency ratio – measured in percentage terms (%)
- Answered calls – measured by volume of calls
- Unanswered calls – measured by volume of calls
- Failed calls – measured by volume of calls
- Mean conversation time – measured in minutes and seconds
- Mean holding time per seizure – measured in minutes and seconds
- Total conversation time – measured in minutes and seconds
All data is measured on a per trunk group or destination level, which is measureable by hour, by day, by week, by month and by year.
5.10.4. Data Presentation and Reporting
All data is displayed near real-time, up to the previous day. Customers can generate their own customised reports. Historical data can be selected with start and end date/time. All reports can be exported in .pdf, .xls and in addition can be sent automatically via e-mail. Customers can find further information on the VoIP/Voice statistics from the Online Performance reporting user guide for SIP Trunking, which is available from their account manager or downloaded from Colt Online.
6. Capability Variation Across Countries
Colt provide service currently in 29 countries. Due to differing regulatory environments and country capability the feature support and geographic coverage varies by country.
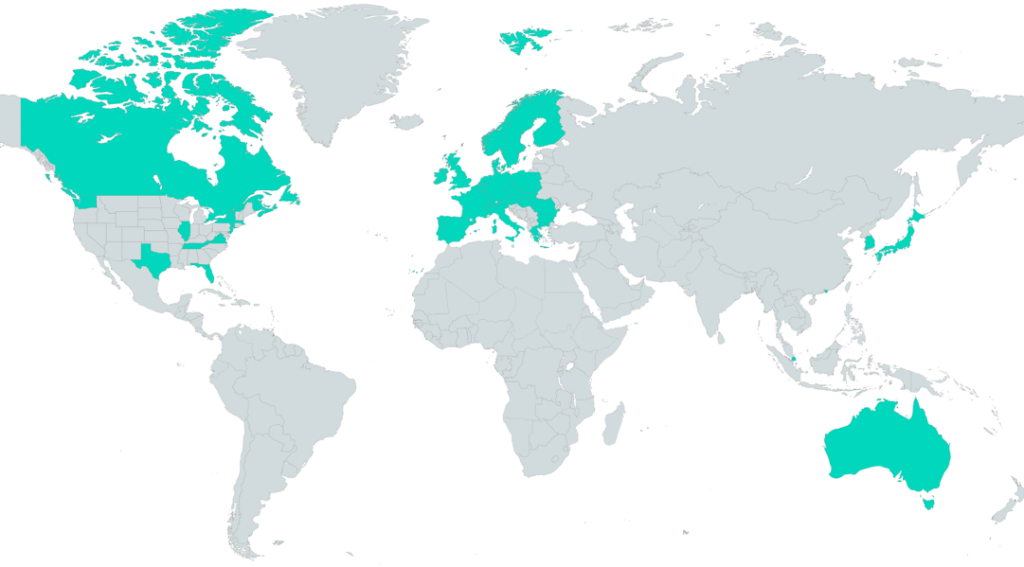
France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Austria, Belgium, Ireland, United Kingdom, Denmark, Netherlands, Germany, Sweden, Switzerland, Japan, Australia, Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, Greece, Hong Kong, Hungary, Luxembourg, Norway, Poland, Romania, Singapore, Slovakia, South Korea, USA:NY, NJ, FL, TN, MA, VA, WA, TX, IL
Figure 6.1. SIP Trunking Overview
The contents of this guide generally apply to the following 13 countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom except where otherwise stated.
Not all features are available in the remaining 16 countries : Czech Republic, Finland, Luxembourg, Norway, Poland, Slovakia, Romania, Japan, Singapore and Hong Kong, Canada, Australia, US (New Jersey, Florida, Tennessee, Massachusetts, Virginia ,Washington, New York and Texas) ,South Korea, Hungary and Greece. Therefore, the service features vary compared to the standard Colt SIP Trunking in existing 13 Colt countries. A service design is required to be defined with the Colt Technical Sales team to ensure customer requirements can be met. For example, online performance reporting is not currently available for service in these countries. Also billing currency is Euros for these countries except Norway which is Norwegian Krone and Japan which is Yen (NB Colt offers the capability for the invoice to be settled in the local currency of the country from which it is issued, for example, invoices issued in the UK can be settled in GBP).
7. Service Assurance
Colt provides a high level of service assurance:
The core network is proactively monitored
• A local language help desk is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week
• Colt Online provides a web-based portal that enables customers to view bills and trouble tickets
Service assurance includes:
• Customer service
• Service Level Agreement
• Colt Online
• Service monitoring
• Planned maintenance
7.1. Customer Service
Colt has a high quality voice network that enables the provision of an annual target service availability. The target availability depends on the service taken and the location of customer sites. The fault help desk is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Customers can report a fault at any time by contacting the Customer Service Centre and speaking to a representative in their local language.
When the service is provisioned, customers are issued with a unique service reference for each circuit that should always be used when reporting faults. The contact number for fault reporting is specified in the handover pack.
7.2. Service Level Agreement
Colt offers a comprehensive service level agreement with the SIP Trunking service, which pays compensation if agreed targets are not met. Our high quality European voice network enables us to provide customers with an annual service availability of up to 99.99%. Customers should contact a Colt Account Executive for more information about the SLA.
The Service Level Agreement (SLA) describes the target for service delivery, restoration and quality for Colt SIP Trunking. It is a separate document which forms part of the customer contract pack.
It is important to note that for service delivered other than via dedicated connections the principle Service Level Agreement is the availability of the Voice platform itself and not the end to end service. For services delivered over a Colt data service, then the SLA for that service applies between the platform and the customer premises. For the voice dedicated connections an end to end SLA from customer premises to the PSTN is provided.
7.3. Colt Online
Colt Online is an intuitive, user-friendly application enabling new and existing Colt customers to interact with Colt via a secure Internet connection without the need to speak to a Customer Service Agent or Account Executive.
Every Colt Online customer is provided with an administrator account for a defined user within their organisation. This administrator has full access to the available features for all their customer accounts and sub accounts, including:
- Search and view any bill from the previous six months in .pdf format*
* Not available in Switzerland due to data protection legislation
- View the status of any order in the delivery process
- View the status of any ticket (covering faults, enquiries, service requests) in real-time
- Search and view all live services
- View an account dashboard, summarising the four features above
7.4. Service monitoring
The SIP core network is proactively monitored and maintained by Colt. For Dedicated Access, Colt IP VPN, Colt IP VPN via NNI the service is proactively monitored and maintained by Colt on an end-to-end basis, including the access circuit and the CPE router, SIP Trunking core network, and termination points to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). This means that Colt proactively instigates remedial action when a fault is detected by the Colt monitoring systems. For 3rd Party Internet connected customers, only the SIP core network and termination points to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) are proactively monitored.
7.5. Service Maintenance
When planned works are required, customers will normally be notified in advance as per the following timelines:
- Five working days – Non-Service-Affecting planned works and standard planned work (routine maintenance)
- 15 to 17 days – Service-Affecting planned works
Typically, planned works occur after 20:00 GMT on weekdays. For emergency changes, Colt endeavours to give four working days’ notice; however, on some occasions, this is not viable and the work will be done in much shorter timescales with supporting justification and reasons.
8. Charges and Billing
8.1. Charging Structure
Colt SIP Trunking is charged on the following basis:
- Professional Services activities undertaken for the customer (e.g. consultancy / design work)
- Installation fee (one-off)
- Service rental fee, where applicable
- Voice tariff – usage based minutes charges (based upon in-country tariffs)
- Additional features
- Moves, Adds, and Changes
8.2. Invoicing
Customers are invoiced either on a monthly or quarterly basis, subject to the commercial terms agreed with Colt. Invoices are sent via post to customers in paper format, with the option to have invoices delivered electronically via email. Invoices are also archived (up to 6 months only) on the Colt online customer portal.
NOTE: Separate invoices are generated from each country where services are delivered to customers.
9. Call Termination China
9.1. Spam Calls
The China telecom authority impose very stringent criteria to all China telecom operators that no spam/phishing calls can be terminated otherwise their license will be in jeopardy.
They define spam calls very loosely which is very difficult for foreign operators to accept.
However, they won’t hesitate to block any number or even the trunk if they find such spam calls excessive.
The calls may originate from a legitimate A-Nr but they will still block it because they suspect those are phishing calls ( i.e. content of the call is bad ).
9.2. Black List
Both the Chinese government and network operators maintain a black list of A-Nr and won’t treat any traffic stream differently.
Our traffic already caused two major (non-Chinese) suppliers being blocked by one of the China carriers for a period of 1-2 weeks.
Another wholesaler has been also blocked by China Unicom for some weeks as well.
In conclusion, China operators will block whatever they consider suspicious. No appeal is possible.
They care about complaint and penalty from China government more than inbound traffic revenue.
Appendix A – Signalling Number Formats
The formats defined here address the default formats for national, and international numbers where appropriate, for the Called and Calling Party Numbers contained in signalling to and from the VoIP Access platform. Special numbers (eg. Emergency numbers) are exceptions and follow local formats.
For successful operation these formats should be followed for all number types:
| Country | Called # | Calling # |
| Austria | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Belgium | NSN | Variable |
| Denmark | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| France | 0+NSN | 0+NSN CC+NSN |
| Germany | NSN | 0+NSN CC+NSN |
| Ireland | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Italy | NSN | 0+NSN CC+NSN |
| Netherlands | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Portugal | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Spain | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Sweden | NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
| Switzerland | NSN | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN |
| UK | 0+NSN | NSN CC+NSN |
DDO Formats:
| Country | Called # | Calling # |
| Austria | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | 0+NSN |
| Belgium | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Denmark | NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| France | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Germany | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Ireland | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Italy | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Netherlands | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Portugal | NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Spain | NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Sweden | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| Switzerland | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
| UK | 0+NSN 00+CC+NSN | NSN |
Key:
NSN – National Significant Number : significant digits without leading zero (e.g. For dialled number: 0170996465; the NSN is : 170996465 and 0+NSN is: 0170996465).
CC – Country Code : digits defining destination or origin country of the call (e.g. for dialled number 0033170996465; the CC+ NSN is: 33170996465 and 00+CC+NSN= 0033170996465).
E.164 – standardised format with leading “+” (e.g. for dialled number 0033170996465; the E.164 is “+3317099646)
